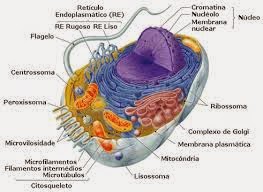
Para fazer com que a insulina seja totalmente bioativa, as células beta pancreáticas iniciam a síntese do precursor da insulina, ou seja, a pré-pro-insulina, no lado citosólico do retículo endoplasmático (RE), após o que se submete a translocação co-e pós-tradução através da membrana do retículo endoplasmático (RE). A pré-pró-insulina é clivada pela peptidase sinalizando para formar a pró-insulina que se dobra no lado luminal do retículo endoplasmático (RE), que formam três ligações dissulfureto evolutivamente conservadas. A pró-insulina adequadamente enrolada forma dímeros e saídas a partir do retículo endoplasmático (RE), o tráfico através do complexo de Golgi em grânulos secretores imaturos em que o peptídeo C é endoproteoliticamente excisada, permitindo uma insulina totalmente bioativa de 2 cadeias para, finalmente, ser armazenada em grânulos maduros para a secreção de insulina. Embora a biossíntese de insulina tem sido intensamente estudada nas últimas décadas, os primeiros eventos, incluindo entrada da pró-insulina e saída do retículo endoplasmático (RE), foram relativamente escassos. No entanto, nos últimos 5 anos, mais de 20 novas mutações no gene da insulina foram relatadas causando uma nova síndrome denominada diabetes induzida por INS-gene mutante da Juventude (MIDy). Embora esses mutantes não tenham sido completamente caracterizados, a maioria deles afeta a entrada de pró-insulina e saída da retículo endoplasmático (RE). O retículo endoplasmático (RE) é um tipo de organela nas células de organismos eucarióticos, que formam uma rede interligada de sacos achatados, fechados por uma membrana ou tubos conhecidos como cisternas. As membranas do RE são contínuas com a membrana exterior do invólucro nuclear. O retículo endoplasmático ocorre na maioria dos tipos de células eucarióticas (uma célula eucariótica possui núcleo verdadeiro, definido e protegido pelo envoltório nuclear) que contém um ou mais nucléolos. É constituída por muitas organelas citoplasmáticas, ao contrário das células procarióticas.
E podem ser animais ou vegetais. (de acordo com os cientistas as células eucarióticas surgiram a partir das procarióticas, que são células relativamente mais simples), incluindo as mais primitivas, mas está ausente nas células sanguíneas vermelhas e espermatozóides. Existem 2 tipos de retículo endoplasmático, retículo endoplasmático rugoso (RER), e retículo endoplasmático liso (REL). A (citosólica) face exterior do retículo endoplasmático rugoso é repleta de ribossomos, que são os locais de síntese de proteínas. O retículo endoplasmático rugoso é especialmente importante em células tais como os hepatócitos onde ocorre a síntese de proteína ativa. O retículo endoplasmático liso não tem ribossomos e funções em metabolismo lipídico, metabolismo de carboidratos e de desintoxicação e é especialmente abundante no fígado de mamíferos e células das gônadas.
*Quão grave e comprometedora é a associação entre a obesidade abdominal e a incidência de diabetes tipo 2!
Em média, observou-se que a obesidade abdominal aumenta o risco de diabetes tipo 2, mais que o dobro. Todas as medidas utilizadas para capturar a obesidade abdominal, mostram uma forte relação com a incidência de diabetes de tipo 2. Os médicos podem usar uma simples medida de obesidade abdominal para identificar pacientes com maior risco de desenvolver diabetes tipo 2. Orientações eficazes de novas drogas terapêuticas em relação aquelas com maior risco podem ser muito melhoradas através da medição sistemática da circunferência da cintura. A prevenção e tratamento da diabetes é um problema de saúde pública em muitos sistemas de saúde. Há uma ampla literatura referindo-se à obesidade como um fator de risco para o desenvolvimento de diabetes.
Estes estudos têm utilizado o índice de massa corporal (IMC) como a medida da obesidade. No entanto, é cada vez mais reconhecida que para uma dada IMC, central, em vez de inferior a distribuição de gordura corporal, confere um maior risco de complicações cardiovasculares e metabólicas da obesidade. Schmidt et al. citam estudos que remontam a 1956, indicando a importância da associação entre a relação cintura-quadril (RCQ) e diabetes tipo 2. O objetivo desta revisão foi avaliar a evidência quantitativa sobre a relação entre a obesidade abdominal e a incidência de diabetes tipo 2 em homens e mulheres, e para examinar a utilidade relativa das diferentes medidas de obesidade abdominal. Um total de 119 artigos foram identificados e selecionados por relevância, por título e resumo. Um subgrupo de 20 artigos relevantes foi incluído na revisão. Os estudos foram incluídos na análise, onde eles examinaram o relacionamento entre pelo menos uma medida de obesidade abdominal, e o desenvolvimento da diabetes tipo 2 ao longo do tempo. Medidas de obesidade abdominal consideradas na avaliação foram: a circunferência da cintura (CC), a relação cintura/quadril (RCQ), a circunferência ilíaca (CI) e a área de gordura intra-abdominal (AGIA). O IMC não foi considerado uma medida de obesidade abdominal. Não é difícil compreender que um demanda de nutrientes maior do que a necessidade para a sobrevivência irá acumular tanto hidrato de carbono simples como o composto no sentido de estimular todos os sistemas produtores de insulina e afins a chegarem a exaustão e, por conseguinte ao acúmulo de gordura ter o efeito de um gatilho que comprometerá diversos órgãos vitais e, por conseguinte se fizermos uma analogia grosseira com um Iceberg, não devemos nos esquecer que é “ipsis litere” uma verdade inquestionável,
pois 7/8 do Iceberg não aparece na superfície, os Icebergs que vemos externamente representam apenas 1/8 do desastre anunciado, crônico e mortal. Obesidade intra-abdominal e diabetes mellitus tipo 2.
ABDOMINAL OBESITY AND DIABETES TYPE 2; HORMONE ENDOCRINE PANCREAS - INSULIN.
THE DIABETES AND INTRA-ABDOMINAL OBESITY: THE GENE OF HUMAN INSULIN LAYS IN SHORT ARM OF CHROMOSOME 11 A SET SINGLE TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS FOUND IN CORE CELL ACTIVE A TRANSCRIPT OF PRE-mRNA, PRO-INSULIN AND INSULIN GENE. PHYSIOLOGY-ENDOCRINOLOGY-NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY-GENETICS-ENDOCRINE-PEDIATRICS (SUBDIVISION OF ENDOCRINOLOGY): DR. JOÃO SANTOS CAIO JR. ET DRA. HENRIQUETA VERLANGIERI CAIO.
GENESIS: A precursor molecule, pre-pro-insulin, a peptide of molecular weight MW 11.500, is translated from messenger RNA (mRNA) pre-pro-insulin in the granular endoplasmic reticulum of pancreatic cells. Microsomal enzymes break the pre-pro-insulin in proinsulin (MW 9.000) almost immediately after synthesis. The pro-insulin is transported to the Golgi apparatus where the storage of the Clathrin-coated secretory granules occurs (Clathrin is composed of six subunits -3 heavy chains of 91 kDa and 3 light chain protein, 23-27 kDa), which plays an important role in the formation of membranous vesicles within eukaryotic process, since they include proteins signaled by the mannose-6-phosphate sugar which adheres digestive proteins derived from the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) in face CIS Golgi complex. Most vesicles carriers leaving the endoplasmic reticulum, and in particular the rough endoplasmic reticulum, are transported to the Golgi apparatus, where they are modified, sorted and sent toward their final destinations. The organelle is present in most eukaryotic cells, but tends to be more prominent in the cells of organs responsible for secretion of certain substances, such as pancreas, pituitary and thyroid glands. A pile of tanks has four functional regions: the CIS-Golgi, medial-Golgi, endo-Golgi and trans-Golgi network. Trans face is concave face, which releases vesicles to the plasma membrane, while the CIS surface is convex and received carriers from other vesicles intracellular organelles.
The protein network forms a polyhedral (in the shape of a ball) composed of many molecules, coating the vesicle as it is formed. Besides helping in the biogenesis of vesicles, the Clathrin seems to be involved also in the process of addressing these vesicles.). Insulin is a hormone essential for maintaining metabolic homeostasis in the body. To make the fully bioactive insulin, pancreatic beta cells prime the synthesis of the precursor of insulin, pre-pro-insulin, the cytosolic side of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) after it undergoes translocation co-and posttranslational through the membrane endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The pre-pro-insulin is cleaved by signal peptidase to form pro-insulin bending on the luminal side of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), which form three disulfide bonds evolutionarily conserved. The pro-insulin properly folded forms dimmers and exits from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the Golgi apparatus trafficking through in immature secretory granules in which the C-peptide is excised endoproteolytically allowing fully bioactive two-chain insulin to ultimately be stored in granules to mature insulin secretion. Although the biosynthesis of insulin has been extensively studied in the past decades, the first events, including pro-insulin entrance and exit the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) are relatively scarce. However, in the last five years, more than 20 new mutations in the insulin gene were reported to cause a new syndrome called induced mutant INS gene-Youth (MIDy) diabetes. Although these mutants have not been fully characterized, mostly affects the pro-insulin inlet and outlet of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a type of organelle in the cells of eukaryotic organisms, which form a network of flattened interconnected bags, closed with a membrane known as tanks or pipes. The ER membranes are continuous with the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope. The endoplasmic reticulum occurs in most types of eukaryotic cells (eukaryotic cell has a central nucleus (nucleus defined and protected by the nuclear envelope), which contains one or more nucleoli. It is composed of many cytoplasmic organelles, contrary to prokaryotic cells.
The ER may be animal or plant. (According to scientists eukaryotic cells arose from prokaryotic, that are relatively simple cells), including the earliest, but is absent from the red blood cells and sperm. There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum, rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). It's (cytosol) external face of the rough endoplasmic reticulum is filled with ribosomes which are the sites of protein synthesis. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is important in particular cells such as hepatocytes that active protein synthesis occurs. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes do not have functions in lipid metabolism, carbohydrate metabolism and detoxification, and is especially abundant in mammalian cells but it is absent in the liver and the gonads.
*How severe and compromising is the association between abdominal obesity and the incidence of type 2 diabetes!
On average, raised - that abdominal obesity increases the risk of type 2 diabetes, more than twice. All the measures used to capture abdominal obesity, show a strong relationship with the incidence of type 2 diabetes. The Doctors can use a simple measure of abdominal obesity to identify patients at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes guidelines effective new drugs therapeutic relationship in those at high risk can be greatly improved through the systematic measurement of waist circumference. The prevention and treatment of diabetes is a public health problem in many health care systems. There is an extensive literature referring to obesity as a risk factor for developing diabetes. These studies have used the body mass index (BMI) as a measure of obesity. However, it is increasingly recognized that for a given BMI, central, instead of the lower body fat distribution, confers an increased risk of cardiovascular and metabolic complications of obesity. Schmidt et al. cite studies that date back to 1956, indicating the importance of the association between waist-hip ratio (WHR) and type 2 diabetes.
The objective of this review was to evaluate the quantitative evidence on the relationship between abdominal obesity and the incidence of diabetes type 2 in men and women, and to examine the relative utility of different measures of abdominal obesity. A total of 119 articles were identified and selected for relevance by title and abstract. The subgroup of 20 relevant articles were included in the review. The studies were included in the analysis where they examined the relationship between the at least one measure of central obesity and the development of type 2 diabetes over time. The abdominal obesity measures considered in the assessment were: waist circumference (WC), waist-hip ratio (WHR), iliac circumference (IC) and area of intra-abdominal fat (AIBA). The BMI was not considered a measure of abdominal obesity. It is not difficult to understand that a greater demand for nutrients than the need for survival will acumulate both simple carbohydrate like compound to stimulate all producers of insulin and related systems to reach exhaustion and therefore the accumulation effect a elected trigger that will jeopardize many vital organs and therefore if we make a rough analogy with an iceberg, we must not forget that it is "litere Ipsis" an unquestionable truth, for 7/8 not appear on the surface, Icebergs we see externally is only 1/8 chronic and deadly disaster. The intra-abdominal obesity and the type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Dr. João Santos Caio Jr.
Endocrinologia – Neuroendocrinologista
CRM 20611
Dra. Henriqueta V. Caio
Endocrinologista – Medicina Interna
CRM 28930
Como saber mais:
1. Pesquisas anteriores sugerem que as crianças que sofrem de várias transições na estrutura familiar podem apresentar resultados de desenvolvimento piores do que as crianças criadas em famílias estáveis com os dois pais e os irmãos, talvez até mesmo criados com famílias monoparentais estáveis...
http://hormoniocrescimentoadultos.blogspot.com
2. No entanto, várias transições e os resultados negativos das crianças podem estar associados a fatores causais comuns, tais como comportamentos e atributos antecedentes dos pais...
http://longevidadefutura.blogspot.com
3. Usando uma de duas gerações para a pesquisa nacionalmente representativa, longitudinal, que inclui informações detalhadas sobre o desenvolvimento comportamental e cognitivo da criança, história familiar, e os atributos da mãe antes do nascimento da criança, hipóteses alternativas foram examinadas...
http://imcobesidade.blogspot.com
AUTORIZADO O USO DOS DIREITOS AUTORAIS COM CITAÇÃO
DOS AUTORES PROSPECTIVOS ET REFERÊNCIA BIBLIOGRÁFICA.
Referências Bibliográficas:
Caio Jr, João Santos, Dr.; Endocrinologista, Neuroendocrinologista, Caio,H. V., Dra. Endocrinologista, Medicina Interna – Van Der Häägen Brazil, São Paulo, Brasil; McManus EJ, Sakamoto K, Armit LJ, Ronaldson L, Shpiro N, R Marquez, Alessi DR (Abril de 2005). "O papel que a fosforilação da GSK3 desempenha na insulina e sinalização Wnt definido pela batendo análise" . EMBO J. 24 (8):. 1571-1583 doi :10.1038 / sj.emboj. 7600633 . PMC 1142569 . PMID 15791206; tando JG, Whittaker J, Margetts MB, Whittaker LJ, Kong GK-W, Smith BJ, Watson CJ, Žáková L, Kletvíková E, JJ, Chan SJ, Steiner DF, Dodson GG, Brzozowski AM, MA Weiss, Ward . CW, Lawrence MC (2013) "Como a insulina envolve seu local de ligação principal do receptor de insulina" . Nature 493 (7431): 241-245. doi : 10.1038 / nature11781 . PMC 3.793.637 . PMID 23302862 . resumo Lay - Australian Broadcasting Comissão; Dimitriadis G, Mitrou P, Lambadiari V, Maratou E, Raptis SA (agosto de 2011). "efeitos da insulina em tecido muscular e adiposo". Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract . 93 Suppl 1:. S52-9 doi : 10.1016 / S0168-8227 (11) 70014-6 . PMID 21864752; Bergamini E, Cavallini G, Donati A, Gori Z (outubro de 2007). "O papel da autofagia no envelhecimento: o seu papel essencial no mecanismo anti-envelhecimento da restrição calórica". Ann. NY Acad. Sei. 1.114 .: 69-78 doi : 10,1196 / annals.1396.020 . PMID 17934054; Benziane B, Chibalin AV (2008). "Fronteiras: esquelético regulagem da bomba de sódio muscular: um paradigma translocação" . American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinologia e Metabolismo 295 (3): E553-8. doi : 10,1152 / ajpendo.90261.2008 .PMID 18430962; Clausen T (2008) "O papel regulatório da translocação de Na +-K + bombas no músculo esquelético: hipótese ou realidade?" . American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinologia e Metabolismo 295 (3): E727-8. doi : 10,1152 / ajpendo. 90494.2008 .PMID 18775888; Gupta AK, Clark RV, Kirchner KA (1992). "Efeitos da insulina sobre a excreção renal de sódio". Hipertensão 19 (1 Supl): 178-182. doi : 10,1161 / 01.HYP.19.1_ Suppl.I78 . PMID 1730458; Bento C, Hallschmid M, Hatke A, B Schultes, Fehm HL, Born J, Kern W. (novembro de 2004). "Insulina intranasal melhora a memória em seres humanos". Psychoneuro endocrinology 29 (10):. 1326-1334 doi : 10.1016 / j.psyneuen. 2004.04.003. PMID 15288712; Bento C, Brede S, Schiöth HB, Lehnert H, Schultes B, Born J, Hallschmid M. (2010)."insulina intranasal aumenta a termogênese pós-prandial e reduz os níveis de insulina sérica pós-prandial em homens saudáveis" . Diabetes 60 (1) : 114-118. doi : 10,2337 / db10-0329 . PMC 3.012.162 . PMID 20876713 [Epub'd ahead of print]; Comninos AN, Jayasena CN, Dhillo WS (2014). "A relação entre intestino e hormônios adiposas e reprodução". Hum. Reprod. Atualize 20 (2):. 153-74 doi : 10.1093 / humupd / dmt033 . PMID 24173881; Duckworth WC, Bennett RG, Hamel FG (Outubro de 1998). "A degradação Insulina: progresso e potencial". Endocr. Rev. 19 (5): 608-24. doi : 10,1210 / er.19.5.608 . PMID 9793760; Palmer BF, Henrich WL. "Carboidrato e insulina metabolismo na doença renal crônica" . UpToDate, Inc .
Contato:
Fones: 55 (11) 2371-3337 - 5572-4848 ou 9.8197-4706
Rua Estela, 515 - bloco D - 12º andar - conj 121 e 122 - Paraiso - São Paulo - SP - CEP 04011-002
email: vanderhaagenbrasil@gmail.com
Rua Estela, 515 - bloco D - 12º andar - conj 121 e 122 - Paraiso - São Paulo - SP - CEP 04011-002
email: vanderhaagenbrasil@gmail.com
Site Van Der Häägen Brazil
www.vanderhaagenbrazil.com.br
http://drcaiojr.site.med.br
http://dracaio.site.med.br
João Santos Caio Jr
http://google.com/+JoaoSantosCaioJr
Vídeo
http://youtu.be/woonaiFJQwY
Google Maps:
http://maps.google.com.br/maps/place?cid=5099901339000351730&q=Van+Der+Haagen+Brasil&hl=pt&sll=-23.578256,46.645653&sspn=0.005074,0.009645&ie =UTF8&ll=-23.575591,-46.650481&spn=0,0&t = h&z=17